

geometry, molecular shape, bond angle, and polarity of the ructure and using VSEPR theory (15 a.

Predict the electron pair geometry, molec following molecules by drawing the Lewis structure and us points). Predict the electron pair geometry, molec following molecules by drawing the Lewis structure and us.Ģ.
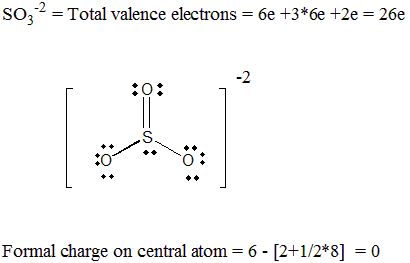
Thus, techniques are available which can identify the geometry of substances. X- ray and neutron diffraction, infrared, Raman and microwave absorption spectroscopy, as well as dipole moment measurements are used to ascertain the three-dimensional structure of a substance. INTRODUCTION The chemical and physical properties of substances are influenced by the way in which valence electrons are distributed and by the three-dimensional shape of the molecule or ion. INTRODUCTION The chemical and physical properties of substances. Two possible resonance structures are shown below. b) Draw all resonance structures for the nitrate ion. a) Explain in your own words what is meant by delocalized electrons. Using the "octet rule" write the Lewis formulas for NF3 and NO3. Does the following Lewis structure represent an anion, a cation, or a molecule? If it represents an ion, what is the charge on the ion? 0: 2. Page l7 Prelaboratory Questions Molecular Geometry 1. Does the following Lewis structure represent an anion, a. Page l7 Prelaboratory Questions Molecular Geometry 1.

Draw a Lewis structure for the molecule or ion which satisfies the rules provided in the procedure C. Calculate the total number of valence electrons in each formula B. These instructions are summarized briefly below. NAME SECTION DATE REPORT FOR EXPERIMENT 17 INSTRUCTOR Lewis Structures and Molecular Models For each of the following molecules or polyatomic ions, fill out columns A through G using the instructions provided in the procedure see- tion.
NAME SECTION DATE REPORT FOR EXPERIMENT 17 INSTRUCTOR Lewis Structures and Molecular Models For each of. b)N, d) CO, c) 0 25-What is the molecular geometry if you have 4 single bonds around the central atom and no lone pairs? I a) Bent b) Tetrahedral c) trigonal pyramidal d) linear 26- Using the following Lewis structure and 3-dimensional structure of CH,OH answer the following questions? H 3- Hybridization of Oxygen b- Hybridization of Carbon CH-C-O bond angle d-HO-C bond angle. 12 13 4 5 6 24- Which of the following molecules have resonance structures? a) NBr.ġ2 13 4 5 6 24- Which of the following molecules have resonance structures? a) NBr. Then, draw the molecule again showing the actual shape and the angles between the atoms as accurately as you can. Complete the following three tables by first drawing a simple sketch of the molecule showing which atoms are attached to each other, the number of bonds between each pair of atoms, and any nonbonding electrons. Date Laboratory Exercises Using a molecular modeling kit, construct models of each of the compounds in.ĭate Laboratory Exercises Using a molecular modeling kit, construct models of each of the compounds in the tables below. Apply VSEPR theory to explain why SiF, is a nonpolar molecule even though it has four polar bonds. ecule even though it has four polar bonds. Predict the electron pair geometry, the molecular shape, and the bond angle for a phosphine molecule, PH, using VSEPR theory. Predict the electron pair geometry, the molecular shape, and the bond angle for a carbon tetrabromide molecule, CBra, using VSEPR theory. Predict the electron pair geometry, the molecular shape, and the bond angle for a carbon.ħ2. Fill in the data table for the molecules listed below in the website. Applied Exerci Pairs and Show Bond Angles are all checked. Make sure that "Real" is selected, and Molecule Geometry, Electron Geometry, Show Lone IV. NAME: 4 0 in molecular, bent geometry present with the band'anglenler, trigonal SECTION: 11. Basic Geometry O lone pair 1 lone pair 4 lone pair's 3 lone pairs 180° Linear <120 Bent or Angular Planar X Tetrahedral << 109° Beat or Angular <109° Trigonal Pyramid < 90° X XI <120° CE- 120☌X Trigonal Bipyramid Sawbore or Seesaw 190° Wa 2 T 90° * T-shape tabedral Square Pyramid Square Planar Objectives Be able to draw electron-dot structure (Lewis dot structure) of molecules, including molecules that are.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
